Sun protection is one of the most essential strategies in skincare for preventing long-term damage, such as premature aging and skin cancer.
However, when choosing a sunscreen, the question arises: is it better to opt for mineral or chemical protection? In this article, we examine the pros and cons of each type, their benefits, and how the industry has advanced in formulation and sensory experience, especially in the area of mineral filters.
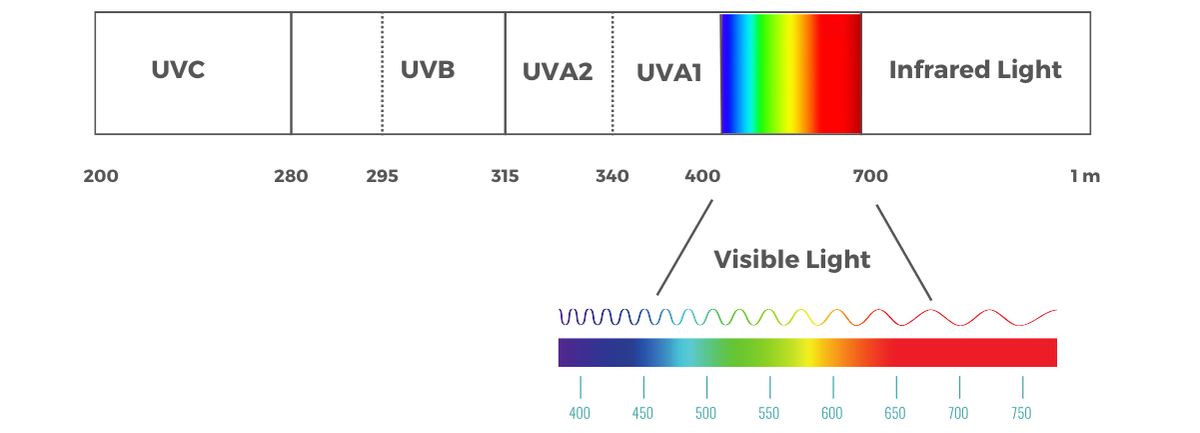
1. Protection Spectrum
- UVA Rays: Associated with premature aging and deep skin damage.
- UVB Rays: Cause sunburn and surface damage.
- High-Energy Visible Light (HEV): Also known as blue light, penetrates deep into the skin, contributing to aging and hyperpigmentation.
- Visible Light (VIS): May impact skin damage, especially in individuals with darker skin tones.
- Infrared-A (IR-A): Penetrates the deepest skin layers and is linked to oxidative stress, contributing to skin aging.
2. Benefits of Sunscreens and Their Impact on Skin and Health
Both mineral and chemical sunscreens help protect the skin from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is associated with skin damage, including:
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Studies have shown that regular sunscreen use significantly reduces the risk of melanoma and other types of skin cancer.
- Reduces Signs of Photoaging: Extended sun exposure without protection can accelerate the appearance of wrinkles and spots. Sunscreen helps maintain younger and healthier skin.
3. What Are Mineral and Chemical Sunscreens?
Sunscreens are mainly divided into two categories based on the type of filter they use:
- Mineral (Physical) Filters: Use natural ingredients like titanium dioxide and zinc oxide. These act by creating a barrier on the skin’s surface that reflects UV rays, forming an external shield to block UV incidence on the body.
- Advantages: Provide broad-spectrum protection against UVA and UVB rays, are ideal for sensitive skin, and start working immediately after application.
- Disadvantages: May leave a white residue on the skin and can sometimes have a thicker texture.
- Chemical Filters: Contain compounds such as avobenzone, octinoxate, and oxybenzone that absorb UV rays within the skin and convert them into heat, which is then released by the skin.
- Advantages: Typically lighter and more transparent in feel, which improves skin sensation and facilitates absorption.
- Disadvantages: Require time to activate, may cause reactions in sensitive skin, and some ingredients have been questioned for their environmental impact, as they affect aquatic life upon reentry into the environment and may pose potential toxicity.
4. Innovation and Advanced Formulations
- Mineral Filters: Zinc oxide is one of the few ingredients that naturally provides broad-spectrum protection. New formulations have reduced the white cast by using microencapsulation and nanoparticle technology; however, the latter remains controversial due to potential risks. ADP’s advanced and patented technology, “CoSmart,” achieves full-spectrum protection with a unique structure that allows the creation of “Non-Nano” particles over 100 nm. This ensures the benefits of mineral filters without the risks associated with nanoparticles, maintaining product efficacy and safety.
- Advances in Sensory Experience: Thanks to innovation in particle development and dispersion technologies like “CoSmart,” today’s mineral filters protect against a full spectrum of radiation and have lighter textures with improved sensory appeal, offering a more pleasant experience and a more transparent appearance on the skin.
5. Sustainability and the Environment
The environmental impact of sunscreens is a significant concern. Chemical ingredients like oxybenzone and octinoxate have been banned in some areas due to their toxicity to marine ecosystems and coral reefs. Mineral filters, on the other hand, tend to be more eco-friendly.
- ADP and Sustainable Development: The cosmetics industry has adopted more sustainable practices, and ADP has been at the forefront of creating mineral sunscreens that are effective and environmentally friendly. ADP uses cleaner extraction and production processes, reducing the carbon footprint and marine impact, along with other formulation and regulatory advantages internationally, advancing the creation of products that benefit both people and the planet.
6. Conclusion: Which Is the Best Option?
Choosing between mineral and chemical sunscreen depends on individual needs and preferences. For sensitive skin, special needs, pediatric skin, individuals undergoing medical treatments, or those seeking an eco-friendly, sustainable option, mineral filters are an excellent choice. For those who prefer a lighter and quickly absorbed texture, chemical filters may be more suitable.
The key is to opt for products that offer full-spectrum protection, use the right amount, and follow reapplication recommendations to ensure effective protection.
The Importance of an Informed Choice
With current trends focused on sustainability, skincare, and multifunctionality, consumers increasingly value transparent labels that honestly describe product benefits and drawbacks. Sun protection options have evolved, and choosing the best fit for each need is essential, considering both skin health and environmental impact.
Making an informed choice means understanding each type of filter, its pros and cons, and how advanced technologies, like ADP’s, offer innovative solutions that combine effective protection and environmental respect.










